China, often referred to as the world’s factory, plays a pivotal role in global manufacturing. The first half of 2024 has seen significant shifts in the manufacturing sector, with implications that resonate far beyond its borders. In this blog post, we will delve into the key trends observed in China’s H1 manufacturing data, explore the underlying factors, and discuss the broader implications for the global economy.
Overview of Growth Metrics
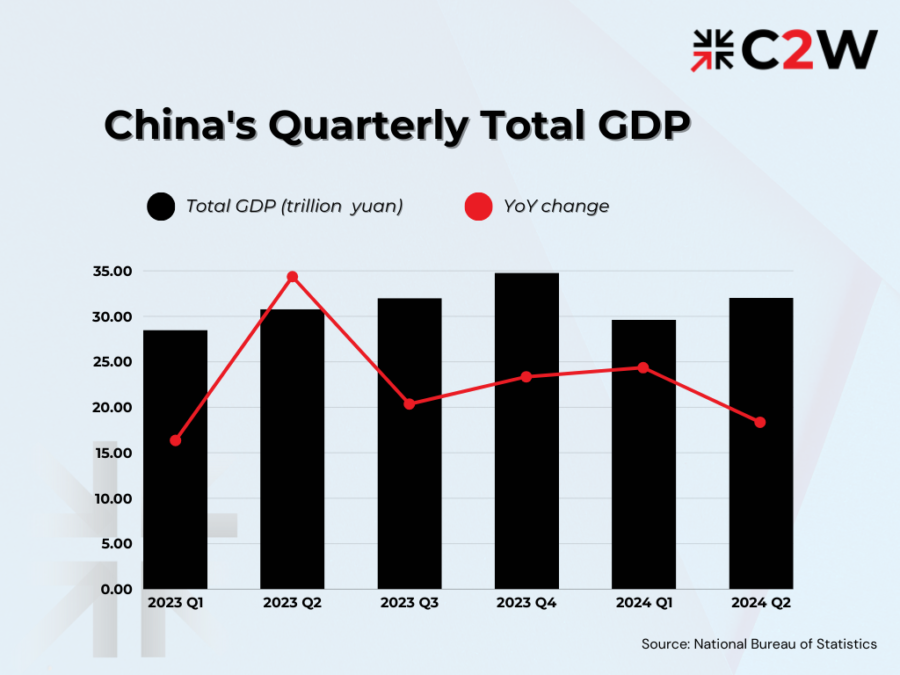
In the first half of 2024, China’s gross domestic product (GDP) reached approximately 61.68 trillion yuan (approximately 8.65 trillion U.S. dollars), according to data from the National Bureau of Statistics. This represents a 5% year-on-year growth. Specifically, the GDP grew by 5.3% in the first quarter and by 4.7% in the second quarter compared to the same periods in the previous year.
These figures reflect a steady economic recovery following the challenges posed by global economic uncertainties. As China navigates through ongoing economic reforms and global dynamics, maintaining this stability will be crucial for sustaining long-term growth and development.
Export Dynamics and Global Influence
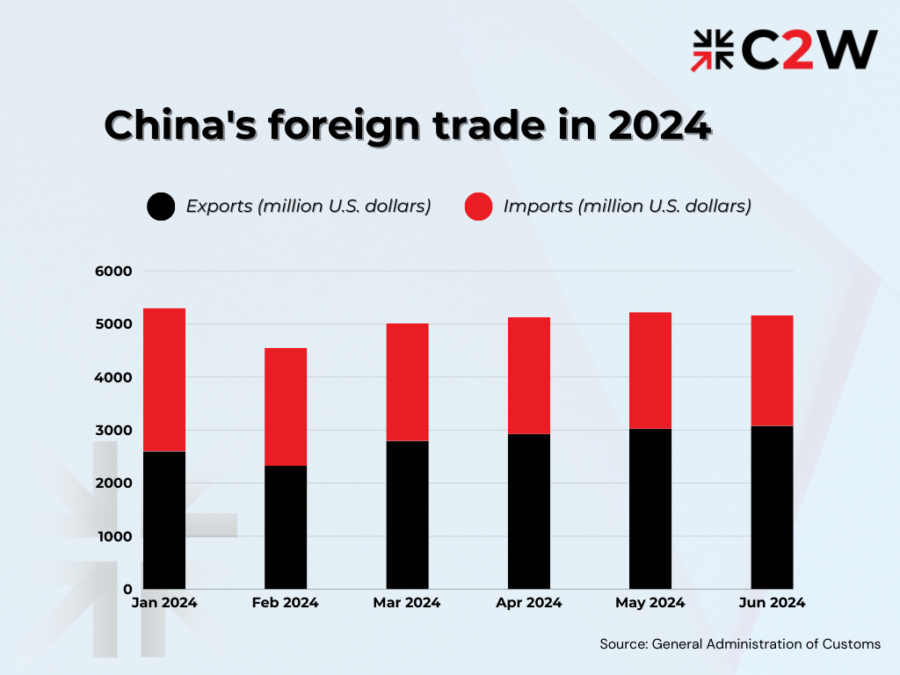
China continues to play a pivotal role in global supply chains, with its exports demonstrating robust performance in various sectors. According to the General Administration of Customs, from January to June, the country’s goods trade volume expanded by 6.1% year-on-year, reaching 21.17 trillion yuan (approximately 2.97 trillion U.S. dollars). This marks the first time China’s foreign trade has surpassed 21 trillion yuan for this period, setting a new record. In particular, exports surged to 12.13 trillion yuan, marking a 6.9% increase, whereas imports also saw growth, rising by 5.2% to reach 9.04 trillion yuan.
Overall, the first half of this year showcased China’s foreign trade resilience and vitality, with the second quarter seeing a 7.4% increase in total imports and exports compared to the previous year. This growth rate surpasses the 4.9% seen in the first quarter of this year and the 1.7% in the fourth quarter of last year, highlighting China’s strong performance in global trade.
Looking ahead to the second half of the year, the outlook for China’s foreign trade development remains notably intricate. Key factors include unstable growth in external demand, uncertainties in the intensity and sustainability of inventory replenishment in major markets, and rising disruptions from geopolitical tensions, trade barriers, and escalating shipping costs. As a result, businesses continue to navigate considerable uncertainties in order acceptance and contract fulfillment.
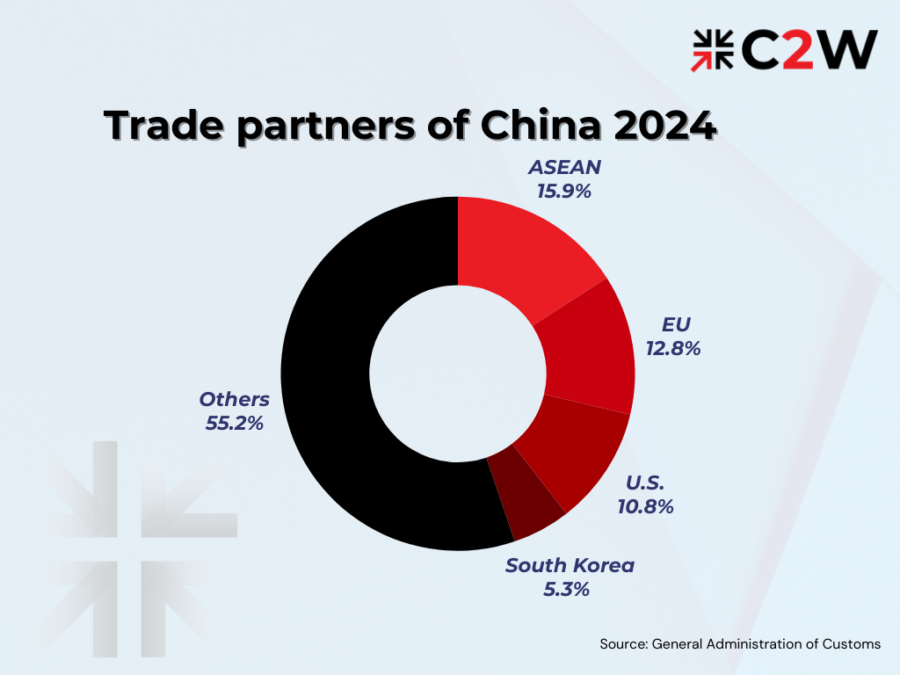
In terms of regional trade, the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) continued to be China’s largest trading partner. The total trade volume between China and ASEAN reached 3.36 trillion yuan, marking a 10.5% increase and accounting for 15.9% of China’s overall foreign trade. China’s exports to ASEAN totaled 2.03 trillion yuan, reflecting a 14.2% rise, while imports from ASEAN amounted to 1.33 trillion yuan, up by 5.2%.
The European Union stands as China’s second-largest trading partner. In the past six months, bilateral trade between China and the EU reached 2.72 trillion yuan, marking a marginal decrease of 0.7%. This trade accounted for 12.8% of China’s total trade volume. Specifically, Chinese exports to the EU amounted to 1.78 trillion yuan, reflecting a slight increase of 0.5%. Meanwhile, imports from the EU totaled 938.87 billion yuan, showing a decrease of 2.9%.
The United States ranks as China’s third-largest trading partner. The total trade value between China and the United States was 2.29 trillion yuan, an increase of 2.9%, accounting for 10.8%. Chinese exports to the United States reached 1.71 trillion yuan, reflecting a 4.7% rise, while imports from the United States amounted to 577.97 billion yuan, showing a slight decrease of 2%.
South Korea is the fourth largest trading partner. The total trade value between China and South Korea was 1.13 trillion yuan, an increase of 7.6%, accounting for 5.3%. Specifically, Chinese exports to South Korea amounted to 516.95 billion yuan, reflecting a slight decrease of 0.6%, while imports from South Korea totaled 609.02 billion yuan, showing a notable increase of 15.7%.
Overview of H1 Manufacturing Performance
In the first half of 2024, China’s high-tech manufacturing sector recorded an 8.7% year on year increase in output, as reported by the National Bureau of Statistics (NBS). Industrial production has notably shifted towards smarter and more environmentally friendly practices. Emerging industries and innovative products have emerged as significant drivers of growth. Specifically, the output of smart products such as 3D printing equipment surged by 51.6%, service robots by 22.8%, and smart watches by 10.9%.
During the same period, manufacturing investment saw a significant rise of 9.5%. In specific sectors, investment in high-tech industries surged by 10.6% year-on-year, with high-tech manufacturing and services experiencing increases of 10.1% and 11.7%, respectively. Notably, within high-tech manufacturing, investment in aviation, spacecraft, and equipment manufacturing rose sharply by 38.3%, while computer and office equipment manufacturing also saw a notable increase of 12.1%.
Strategic Insights for Manufacturing Industry
China’s manufacturing industry has shown remarkable resilience and adaptability in the first half of 2024. This section will delve into some of the key trends and sectoral performances that have characterized this period, shedding light on the driving forces behind the observed growth and the future outlook.
Technological Advancements
One of the most prominent trends in H1 2024 was the rapid adoption of advanced manufacturing technologies. Automation, artificial intelligence, and the Internet of Things (IoT) have become integral to production processes, enhancing efficiency and reducing costs.
In 2024, significant scientific and technological advancements have been consistently delivered. China successfully completed the acceptance of its first domestically developed “ground space station,” known as the Space Environment Simulation and Research Infrastructure (SESRI), in February. The sixth C919 jetliner delivered worldwide joined the China Eastern Airlines fleet in May. And in July, China announced that it had developed the world’s first 6G field test network integrating communications and intelligence, allowing deeper integration of communication with artificial intelligence..
Green Manufacturing Initiatives
Sustainability has become a focal point for Chinese manufacturers. In alignment with the national carbon neutrality goals, many companies have implemented green manufacturing practices. Investments in renewable energy, waste reduction, and energy-efficient technologies are not only reducing environmental impact but also improving competitiveness in global markets where eco-friendly products are in high demand.
In H1 2024, the output of new energy vehicles increased by 34.3% year-on-year, and the output of supporting products such as charging piles and automotive lithium-ion power batteries increased by 25.4% and 16.5% respectively. The photovoltaic industry chain is growing well. The output of the main raw materials polycrystalline silicon, monocrystalline silicon, and ultra-white glass for solar industry increased by 55.4%, 43.6%, and 42.8% respectively year-on-year.
Export Market Dynamics
Despite global economic uncertainties, China’s export market remains resilient. Key sectors such as electronics, machinery, and textiles have shown strong performance. Notably, China experienced consistent growth in exports of mechanical and electrical products, including data processing devices, cell phones, and automobiles, which increased by 8.2% to reach 7.14 trillion yuan, constituting 58.9% of the nation’s total exports. Specifically, automobile exports surged by 22.2% year-on-year, totaling 391.8 billion yuan.
China’s strategic trade agreements and initiatives, such as the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), are opening new markets and enhancing trade relationships, further boosting the export-driven growth of the manufacturing sector.
Conclusion
In conclusion, China’s H1 manufacturing data reflects a complex interplay of resilience, innovation, and strategic foresight. As global markets recalibrate, monitoring these trends becomes imperative for stakeholders across industries. The insights gleaned not only inform immediate business strategies but also shape long-term economic outlooks.
If you’re eager to delve deeper into China’s manufacturing sector or seeking an integrated solution to streamline your production processes, contact us at C2W today. As a British-owned and managed manufacturing consultancy since 2005, we bring a unique blend of international standards and local market understanding to our operations. With years of experience, we have refined our capabilities and broadened our network to deliver optimal manufacturing solutions tailored to our clients’ needs.


